Immersive media installations are revolutionizing how we interact with physical and digital environments, creating transformative experiences that captivate audiences worldwide.
From art galleries and museums to corporate spaces and public installations, the integration of cutting-edge technology with creative vision is reshaping our understanding of space, storytelling, and human connection. These installations leverage projection mapping, virtual reality, augmented reality, interactive sensors, and spatial audio to create multisensory environments that blur the boundaries between observer and participant. As technology becomes more accessible and sophisticated, immersive media installations are no longer confined to high-budget venues but are becoming integral to how brands, artists, and institutions communicate their messages and values.
🎨 The Evolution of Spatial Storytelling
The journey of immersive media installations traces back to early experimental art movements, but the digital revolution has accelerated their evolution exponentially. What began with simple light projections and sound installations has transformed into complex, multi-layered experiences that respond to human presence, movement, and even emotional states.
Contemporary immersive installations draw from diverse disciplines including architecture, psychology, computer science, and traditional arts. This interdisciplinary approach creates experiences that engage multiple senses simultaneously, triggering deeper emotional responses and more memorable interactions than traditional media formats.
The shift from passive observation to active participation represents a fundamental change in how audiences consume content. Visitors no longer simply view art or information—they become co-creators of the experience, with their movements, choices, and interactions shaping the narrative in real-time.
Technologies Driving Immersive Transformation
The technical infrastructure behind successful immersive installations combines hardware, software, and creative vision in unprecedented ways. Understanding these technologies reveals the possibilities and limitations of spatial media experiences.
Projection Mapping and Visual Environments
Projection mapping has emerged as one of the most versatile tools for transforming spaces. By precisely calibrating projected images to match three-dimensional surfaces, artists and designers can make static architecture appear to move, breathe, and tell stories. This technology turns buildings into canvases, creating spectacles that attract thousands of viewers and generate significant social media engagement.
Advanced projection systems now offer unprecedented brightness, resolution, and color accuracy, enabling installations in challenging lighting conditions and large-scale venues. Multi-projector setups with edge-blending capabilities create seamless visual experiences across complex architectural features.
Interactive Sensors and Responsive Systems
Motion sensors, depth cameras, touch interfaces, and biometric devices enable installations to respond dynamically to audience behavior. These technologies transform spaces into living environments that acknowledge, adapt, and react to human presence.
Computer vision systems can track multiple individuals simultaneously, creating personalized experiences within shared spaces. This technology allows installations to maintain coherent narratives while responding to individual participants, balancing collective and personal engagement.
Spatial Audio and Sonic Environments
Sound design plays an equally crucial role in immersive installations, though it often receives less attention than visual elements. Spatial audio systems create three-dimensional soundscapes that enhance realism and emotional impact, guiding attention and reinforcing narrative elements.
Modern audio technologies including ambisonics, object-based audio, and directional speakers enable precise control over sonic environments. These systems can create intimate auditory experiences for individual participants while maintaining cohesive soundscapes for larger groups.
🌟 Applications Across Industries and Sectors
Immersive media installations have found applications far beyond traditional art contexts, proving their value across diverse sectors and objectives.
Museums and Cultural Institutions
Cultural venues were among the early adopters of immersive technologies, recognizing their potential to make exhibitions more engaging and accessible. Interactive installations allow museums to present historical narratives in ways that resonate with contemporary audiences, particularly younger visitors accustomed to digital interaction.
These technologies also solve practical challenges, enabling institutions to showcase fragile artifacts through high-resolution digital reproductions while protecting originals. Virtual reconstructions bring destroyed or inaccessible sites to life, offering educational experiences impossible through traditional means.
Retail and Brand Experiences
Forward-thinking retailers have embraced immersive installations as tools for differentiation in an increasingly competitive marketplace. These experiences transform shopping from transactional activities into memorable events that strengthen brand identity and customer loyalty.
Pop-up installations and flagship store experiences use immersive media to communicate brand values, demonstrate product features, and create shareable moments that extend reach through social media. The most successful retail installations balance entertainment value with subtle product integration, avoiding heavy-handed marketing approaches.
Corporate and Educational Environments
Businesses are incorporating immersive installations into offices, conference spaces, and training facilities to enhance communication, collaboration, and learning outcomes. Interactive data visualizations transform abstract information into tangible, explorable environments.
Educational institutions leverage these technologies to create experiential learning opportunities that improve retention and understanding. Complex scientific concepts become accessible through interactive simulations that allow students to manipulate variables and observe outcomes in real-time.
Public Spaces and Urban Design
Cities worldwide are integrating immersive installations into public spaces as placemaking strategies that foster community engagement and cultural vitality. These projects transform underutilized areas into destinations, contributing to urban revitalization and economic development.
Temporary installations during festivals or permanent fixtures in parks and plazas create gathering points that encourage social interaction and civic pride. The most successful public installations consider accessibility, inclusivity, and long-term maintenance from conception.
The Psychology of Immersion: Why These Experiences Resonate
The effectiveness of immersive media installations stems from fundamental aspects of human psychology and perception. Understanding these mechanisms explains why these experiences create such powerful emotional and cognitive impacts.
Presence and Transportation
Well-designed immersive environments create a sense of “presence”—the psychological sensation of being somewhere other than one’s physical location. This phenomenon occurs when sensory inputs align convincingly enough that our brains accept the artificial environment as real, at least temporarily.
This transportation effect temporarily suspends critical thinking, making audiences more receptive to narratives and messages. The emotional responses generated during these states of presence tend to be stronger and more memorable than those produced by traditional media.
Agency and Interaction
Interactive elements satisfy fundamental human needs for agency and control. When installations respond to our actions, they validate our presence and importance within the experience. This feedback loop encourages continued exploration and deeper engagement.
The balance between guided narrative and free exploration significantly impacts user satisfaction. Too much structure feels restrictive, while too little guidance leaves audiences confused. Successful installations provide clear affordances while allowing meaningful choice.
Social Connection and Shared Experience
Many immersive installations create opportunities for social interaction and shared experience, addressing the growing concern about digital isolation. Collaborative installations encourage communication and cooperation, strengthening social bonds through shared discovery.
The communal aspect also enhances memorability—experiences shared with others become part of our social narratives, reinforced through retelling and discussion. This social dimension extends the impact far beyond the immediate encounter.
⚡ Design Principles for Effective Immersive Installations
Creating successful immersive media installations requires careful attention to design principles that balance technical capability with human experience.
Clarity of Purpose and Message
Before technical considerations, designers must establish clear objectives. Is the installation meant to educate, entertain, inspire reflection, or drive commercial outcomes? This foundational purpose should guide every subsequent decision about content, interaction design, and technology selection.
The most impactful installations communicate their core message without requiring extensive explanation. Visual and interaction language should be intuitive enough that audiences understand how to engage within moments of entry.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Truly transformative installations consider diverse audiences from the outset, ensuring experiences remain accessible to people with varying physical abilities, technological literacy, and cultural backgrounds. This commitment to inclusivity expands reach and demonstrates social responsibility.
Accessibility features shouldn’t feel like afterthoughts but should integrate seamlessly into the core experience. Alternative interaction methods, adjustable sensory intensities, and clear wayfinding benefit all users while ensuring no one is excluded.
Balancing Technology and Content
A common pitfall in immersive installation design is prioritizing technical sophistication over meaningful content. Technology should serve the narrative and objectives rather than becoming the focus itself. Audiences remember compelling stories and emotional moments, not technical specifications.
The most memorable installations often use relatively simple technologies in clever, unexpected ways. Restraint and intentionality typically produce better results than technological excess.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementation
Despite their potential, immersive media installations present significant practical challenges that must be addressed for successful implementation.
Technical Complexity and Maintenance
Immersive installations involve numerous interconnected systems that must function reliably in often-challenging environments. Hardware failures, software bugs, and calibration issues can quickly degrade experiences, requiring dedicated technical support and maintenance protocols.
Long-term installations particularly need consideration for component obsolescence, software updates, and evolving audience expectations. Planning for ongoing technical support and periodic refreshes ensures installations remain effective over extended periods.
Budget and Resource Allocation
High-quality immersive installations require significant investment in equipment, content development, installation, and maintenance. Organizations must realistically assess budgets and expected returns, whether measured in visitor numbers, brand impact, or educational outcomes.
Phased implementation approaches can make ambitious projects more financially feasible, starting with core experiences and expanding based on audience response and available resources.
Measuring Impact and Success
Quantifying the success of immersive installations presents challenges beyond simple attendance figures. Organizations should establish metrics aligned with objectives, whether measuring engagement duration, social media reach, learning outcomes, or brand perception changes.
Combining quantitative data with qualitative feedback through observations and interviews provides comprehensive understanding of installation effectiveness and areas for improvement.
🚀 Future Directions and Emerging Possibilities
The field of immersive media installations continues evolving rapidly, with emerging technologies opening new creative possibilities and applications.
Artificial Intelligence and Adaptive Experiences
Machine learning algorithms enable installations to become genuinely adaptive, learning from audience behavior to optimize experiences over time. AI-driven systems can generate unique content variations, ensuring repeat visitors encounter fresh experiences.
Natural language processing allows voice interaction that feels conversational rather than command-based, making installations more accessible and engaging. Computer vision advances enable more nuanced understanding of human emotion and attention, allowing installations to respond with appropriate sensitivity.
Extended Reality Integration
The convergence of physical installations with augmented and virtual reality technologies creates hybrid experiences that leverage the strengths of each medium. Mixed reality installations allow digital content to coexist with physical environments in convincing ways, expanding creative possibilities.
As AR-capable devices become ubiquitous through smartphones and emerging wearables, installations can deliver layered experiences that vary based on how audiences choose to engage—with or without digital augmentation.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Growing awareness of environmental impact is driving innovation in sustainable installation design. Energy-efficient technologies, renewable power sources, and circular economy principles are becoming standard considerations rather than optional enhancements.
Some installations explicitly address environmental themes, using immersive experiences to communicate climate science and inspire conservation action. These projects demonstrate how immersive media can contribute to social and environmental goals beyond entertainment.
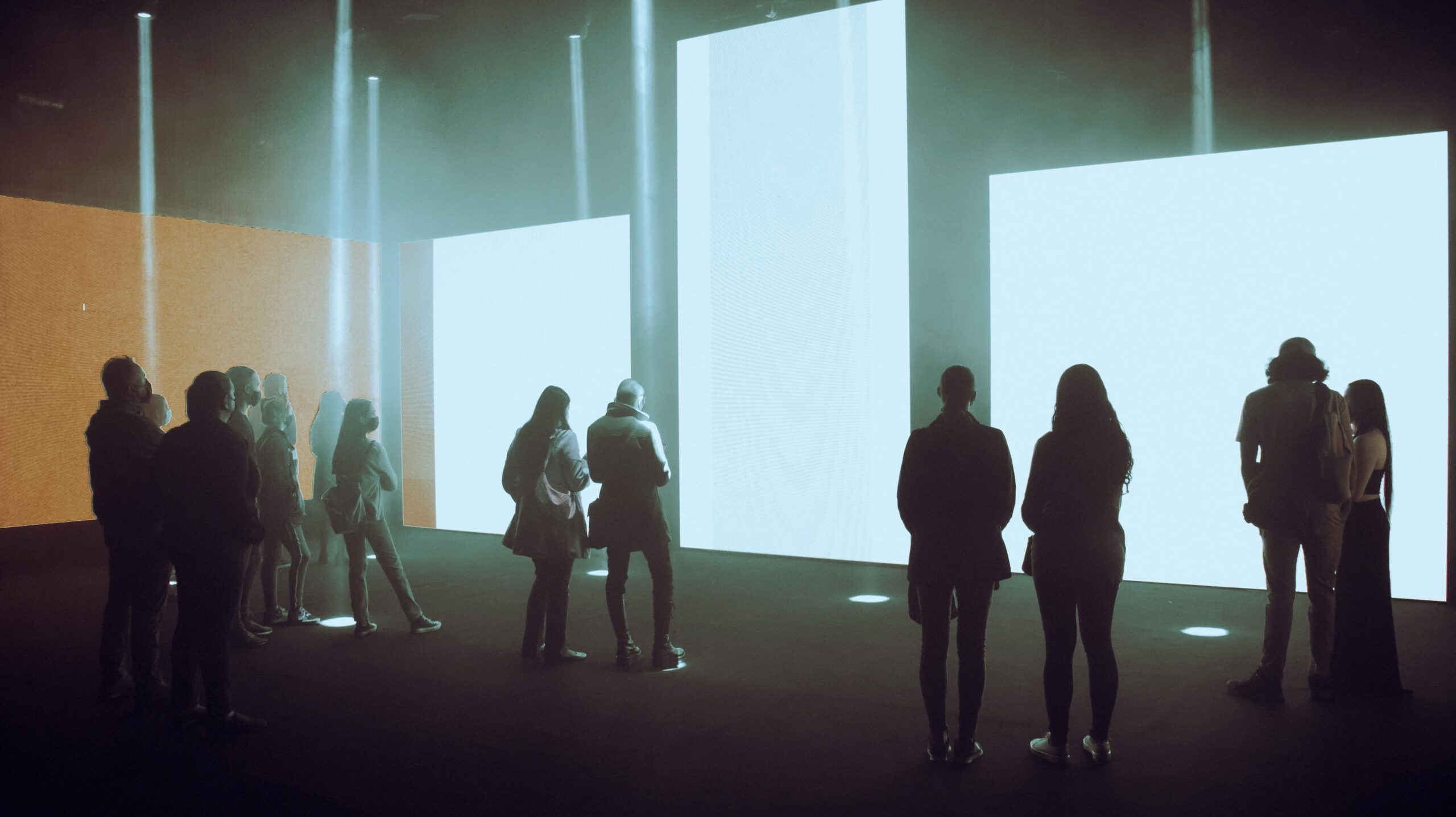

Creating Lasting Impact Through Thoughtful Design
The true power of immersive media installations lies not in their technological sophistication but in their capacity to create meaningful human experiences. When thoughtfully designed with clear purpose, accessibility, and audience needs at the center, these installations transcend novelty to become transformative encounters that shift perspectives and inspire action.
As the technology becomes more accessible and the creative community more experienced, we can expect immersive installations to become increasingly integral to how we communicate, learn, and connect. The spaces we inhabit—whether museums, retail environments, public plazas, or workplaces—will continue evolving into responsive, intelligent environments that adapt to human needs and desires.
The most successful practitioners in this field will be those who maintain focus on human experience rather than technological capability, who design for inclusivity rather than exclusivity, and who recognize that the ultimate goal is not to impress audiences with technical prowess but to create moments of genuine connection, insight, and transformation. The future of immersive media installations is bright, limited only by our creativity and commitment to meaningful engagement.
Whether you’re an artist exploring new creative territories, a business seeking innovative customer engagement, or an institution aiming to educate and inspire, immersive media installations offer unprecedented opportunities to transform spaces and experiences in ways that resonate deeply with contemporary audiences. The key to success lies in balancing technological possibility with human-centered design, ensuring that innovation serves purpose and that spectacle supports substance. 🌐
Toni Santos is an art and culture researcher exploring how creativity, technology, and design influence human expression. Through his work, Toni investigates how innovation and imagination preserve heritage, solve problems, and inspire new forms of creation. Fascinated by the intersection between tradition and digital culture, he studies how art adapts through time — reflecting the human need to remember, reinvent, and communicate meaning. Blending cultural theory, design thinking, and creative history, Toni’s writing celebrates the power of art as a bridge between memory and innovation. His work is a tribute to: The transformative power of creativity and design The preservation of cultural heritage through technology The emotional language that connects art and humanity Whether you are passionate about art, innovation, or cultural preservation, Toni invites you to explore the evolution of creativity — one idea, one design, one story at a time.